|
||||
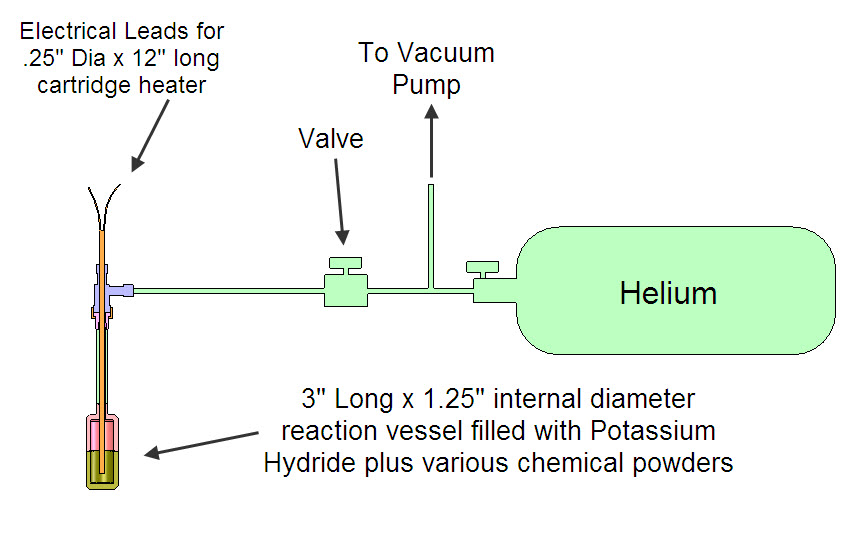
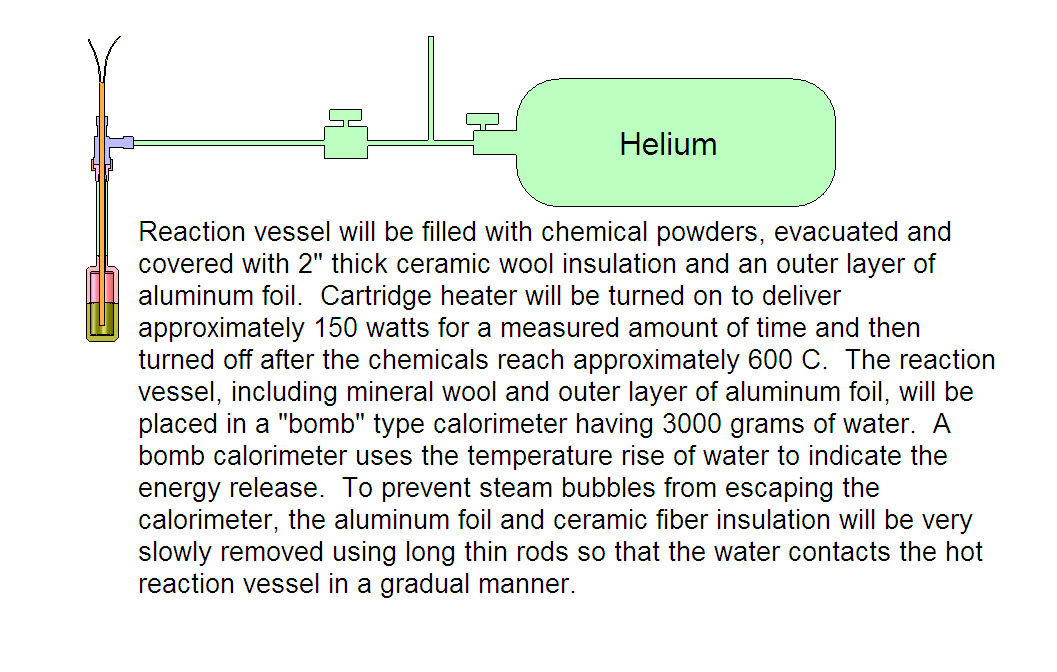
| Experiment #2: Water Bath Calorimetry and the Blacklight Power Process Summarizing the steps for Experiment #2: 1. System components: Reaction Vessel 1.1" ID and 3 inches long internally (45 cc volume) with 300 watt, .25" diameter cartridge heater at center. 2. Put approximately 60 grams (total) of the following chemicals in the Reaction Vessel: Potassium Hydride, Titanium Carbide, Magnesium and Silver Chloride. 2. Cover reaction vessel with 3" of ceramic wool insulation. 3. Heat to 550 C using .25" diameter cartridge heater for a specific (but undetermined at this point) length of time. 4. Turn off cartridge heater and place into 3000 gram bomb type calorimeter and allow water to slowly absorb heat from reaction vessel and insulation. This will be done gradually so that there is no steam produced that could escape. Also, while it is all in the water bath, the mineral wool will be pulled away from the reaction vessel when the reaction vessel reaches a low enough temperature. 5. Use temperature rise of water to calculate the amount of thermal energy released by the reaction vessel and compare to maximum theoretical energy that could be expected given the starting initial chemicals.
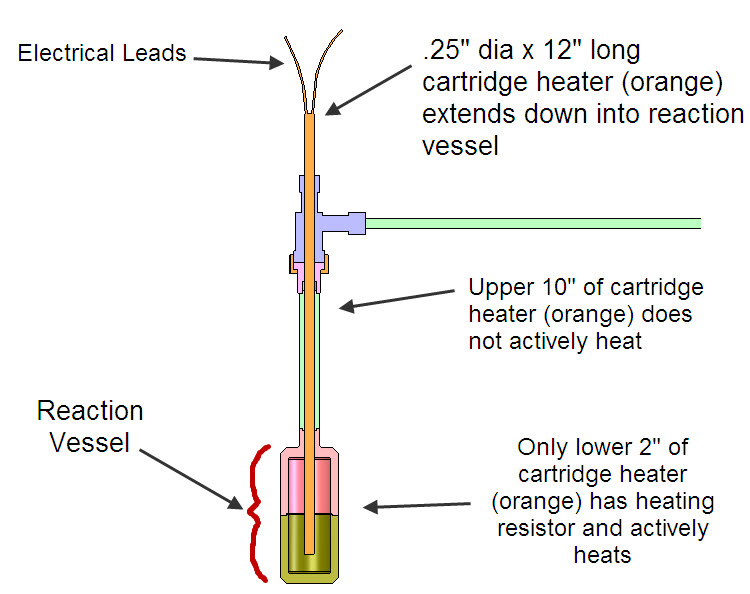
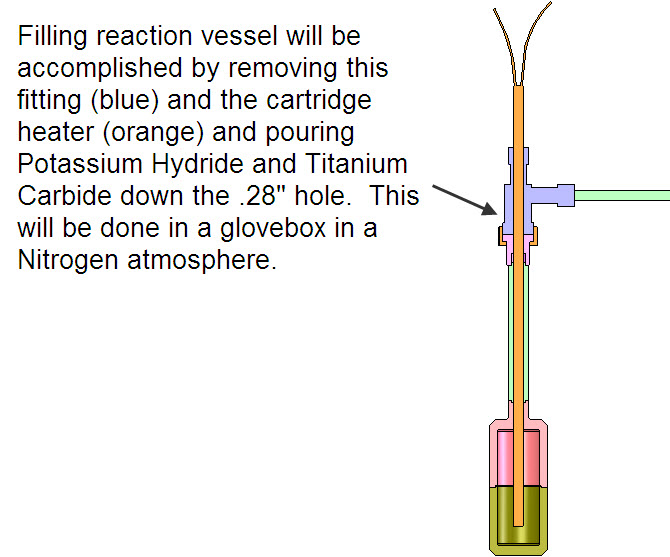
Figure above shows the Reaction Vessel (45 cc) details for Experiment #2. Only the bottom portion of the cartridge heater (about 2 inches) has the heating element inside it. The rest of the cartridge heater only has electrical leads inside of it.
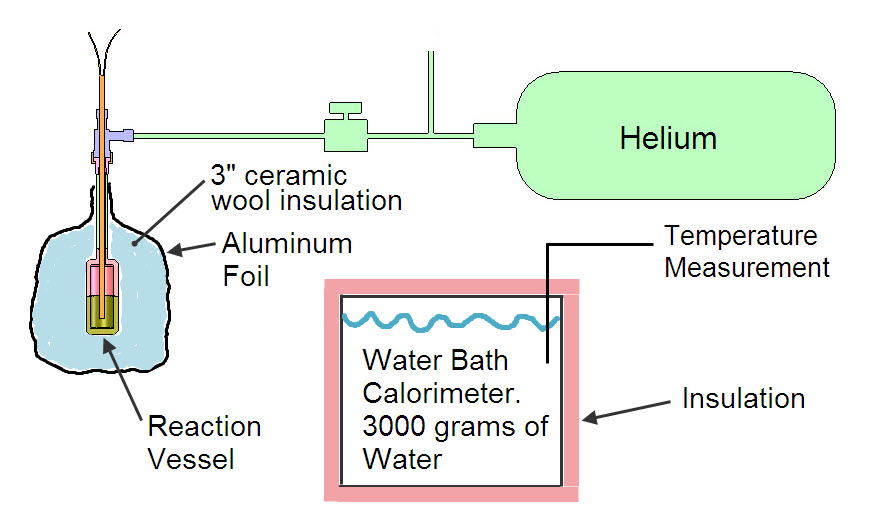
Figure above shows the entire system for Experiment #2 though it does not show the vacuum pump.
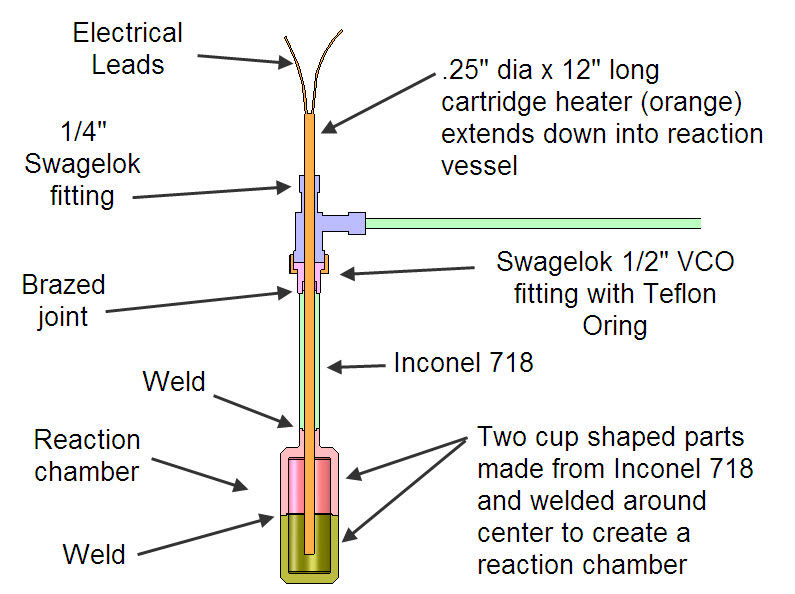
Figure above shows details on the setup of Experiment #2. More details on Experiment #2.
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|